
What are Certificate Authorities & Trust Hierarchies?
While working with Code Signing Certificates, you must have come across the word Certificate Authority or Trusted CAs. Also, you must wonder why everyone focuses so much on selecting a CA. What role does it play?
We have got the answer to all your queries. Let’s get started to understand, What is Certificate Authority and which is the Best Code Signing Certificate Authority. In addition, you will get to know why publishers perform in-depth research in finding a CA.
Understanding Fundamentals: Answer to Some Common What
What is Certificate Authority?
We all hear that you should always purchase an SSL and Code Signing Certificate from an authorized Certificate Authority. But, only a few of us know what precisely a Certificate Authority means.
Certificate Authority is an entity that is responsible for issuing Digital Security Certificates to businesses and individual software publishers. Whenever a software publisher requires a Code Signing Certificate, it submits the CSR document to the Certificate Authority.
You can also consider a CA as the highest in charge, who decides whether you will get the certificate or not. In addition, only a few enterprises are functioning as Certificate Authority. The path to becoming a CA is more challenging than it looks. A firm has to participate in the member program, held by multiple browsers, operating systems, and mobile device-owning companies.
All such institutes verify the organization’s legitimacy and confirm whether it follows all defined regulations. If the firm passes validation, it gets declared a CA with authority to issue digital certificates to other companies.
What is Certificate Authority Hierarchy?
By default, every operating system and browser stores information about legitimate CAs. It leads the systems to check software authenticity by tracing its Chain of Trust.
In the Chain of Trust, authorized CAs and the software publisher resides hierarchically. At the top, you will find Root CA, Intermediate CA, and Software Publisher Certificate at the lowest.
Whenever you try to install any software, operating system, check the publisher’s Code Signing Certificate. Then, it tracks back and matches the Intermediate CA information. Further, it moves to verify the details of Root CA with the Certificate Authority database, which is present by default in the system.
Let’s look at an example.
Below is a snippet of the Cisco Packet Tracer Software Chain of Trust. When you run the software on your machine, you can view the Software Publisher Certificate. And by clicking on the Certificate Path tab, the Chain of Trust will get displayed.
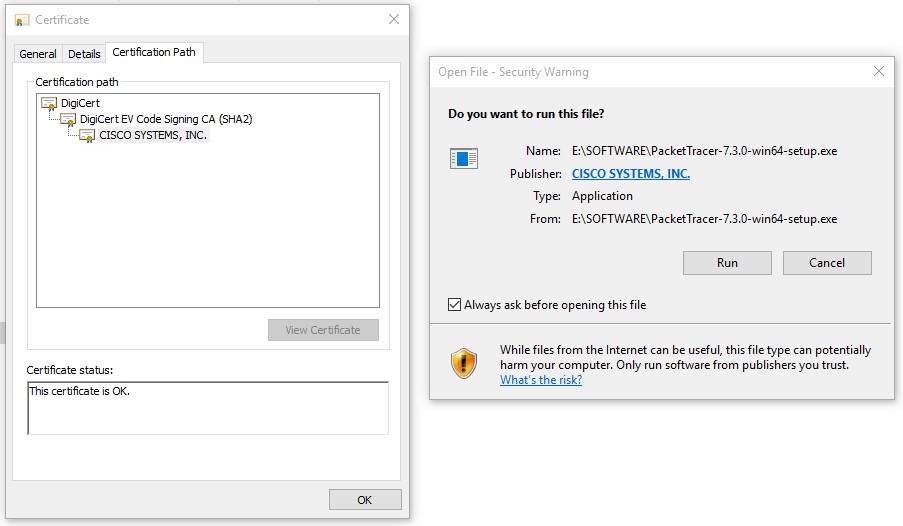
In the above-provided Chain of Trust, DigiCert is the Root Certificate, DigiCert EV Code Signing CA (SHA2) is the intermediate CA and Cisco System Inc. is the publisher. The system starts verifying the certificates from bottom to up to prevent the installation of unauthorized applications.
What is Trust Certificate Authority in Certificate Hierarchy?
Whenever an end-user tries to install software, the operating system verifies whether it can trust the executable file or not. And it gets checked by performing the tracing back operation.
The operating system only trusts the software if it’s coming from an authorized publisher, getting backed up by trustworthy Root CA.
You must be thinking, if the system’s primary focus is on Root CA, then what is the role of Intermediate CA? Let’s understand it.
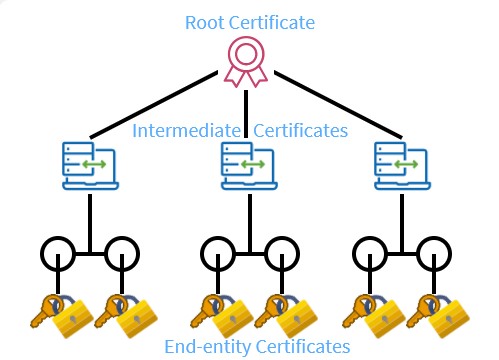
Root CA is the highest authority that completes the requirements to pass the CA membership program. Also, all its details are by-default present in every operating system. Further, its public key is present only in offline mode for security purposes. For instance, if any hacker breaches the software publisher’s certificate and reaches out to the intermediate CA certificate level. Then, being offline would prevent it from moving further, as Root CA’s PKI will not be available online.
In addition, Root CAs don’t directly issue you a Code Signing Certificate. It’s the responsibility of the Intermediate Certificate Authority. Such CAs get assigned by the Root CA to provide security solutions to individual and organizational software publishers.
Hence, the operating system moves from the child branch to the parent branch to establish trust.
Best Code Signing Certificate Authority: The list of some top Trusted CAs
If you search on the internet, you will find numerous Certificate Authorities. All of them will be providing an extensive range of digital security certifications. However, only some have been in the industry for more extended and built their reputation through A+ quality services and products.
The List includes:
- Sectigo (Formerly Comodo)
- GoGetSSL
- DigiCert
- Thawte
- Symantec
- Entrust and much more
All these are the most preferred Root Certificate Authorities, as they comply with all CA/Browser guidelines. Hence, you get the cutting-edge Code Signing Certificate, assuring source code integrity.
Comodo Code Signing or Sectigo Code Signing: Which one to Choose?
While finding a Code Signing Certificate, you will analyze that various vendors have listed Comodo and Sectigo Certificates differently. Although, Sectigo and Comodo are identical, why are products displayed like this?
In recent years, Comodo was rebranded to the name Sectigo after it gets owned by Francisco Partners. After the acquisition, the organization renamed Comodo and launched it as Sectigo. As a result, all the authority of Comodo CA gets transferred to the name Sectigo.
However, the CA authority rights of Comodo also get transferred. But, it continues to provide Code Signing Certificate under its previous and new name, i.e., Comodo and Sectigo.
Hence, if you are confused about selecting between Comodo and Sectigo, you can choose anyone. Both provide the same quality, and their details are available in the in-built operating system database.
Concluding Up
Certificate Authorities are the most reputed entity in the Chain of Trust. Without a CA, you cannot avail of a Code Signing Certificate, as it’s their responsibility to validate your details. Every Certificate Authority aligns with the CA/Browser guidelines, making it a trusted brand across operating systems, browsers, and devices.
Furthermore, you should always purchase digital certificates from reliable CAs, as operating systems trace back the Certificate Hierarchy. It checks your intermediate and root certificate before allowing seamless software installation.
Therefore, to optimize business legitimacy and source code integrity, an authentic Certificate Authority is necessary.
WordPress Development | WordPress Theme Development | PSD To WordPress

